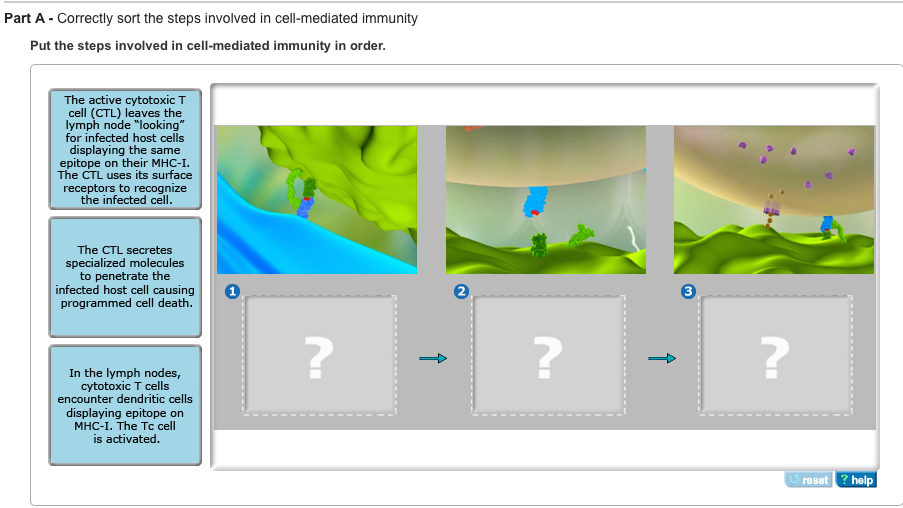
Correctly Sort the Steps Involved in Cell Mediated Immunity
T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. 100 87 ratings correct order 1 In the lymph nodes cytotoxic T cells encounter dendritic cells displa.
Solved Part A Correctly Sort The Steps Involved In Chegg Com
And there are two types of T cells.

. The humoral immune system is also termed antibody mediated immunity and comes in protein chemical form. While the humoral response mainly protects against extracellular pathogens and toxins CMI is responsible for detecting and destroying. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
The active cytotoxic T cell TCL leaves the lymph node looking for infected host cells displaying the same epitope on their MHC-I. The innate immune system is essentially made up of barriers that aim to keep viruses bacteria parasites and other foreign particles out of your body or limit their ability to spread and move throughout the body. Secretion of lymphokines - cytotoxic T cells and activated macrophages generated - these are the effector cells.
I 3 4 1 2a 2b 1 APC processes intracellular pathogen 2 peptides are presented on MHC class I MHC class II 3 APC activates specific T Hcell to become T H1 4 T. This is called acquired immunity and it is of two types. Cell-Mediated Effector Responses Cell-mediated immunity Effector role detect and eliminate cells infected with intracellular pathogens Two types.
T lymphocytes mediate the response. Humoral and cell mediated immunity responses. There are several different types of T cells including helper cytotoxic memory and regulatory T cells.
A variety of effector T-cells sub-types are generated during an Adaptive Response and are responsible for either direct killing of infected cells or induction of effector functions by other immune cells. After the primary immune response fails to handle the pathogen the adaptive immune system causes a secondary immune response. Via phagocytosis they engulf and digest the harmful pathogens that contain.
Cell-mediated immunity is primarily driven by mature T cells macrophages and the release of cytokines in response to an antigen. Cellular response to most intracellular pathogens. Cellular immunity protects the body through.
When a foreign pathogen an infectious particle like a bacterium is detected in the body specific white blood cells called macrophages are called in as the first line of defense. Humoral Immune Response 3. The key cells of the adaptive immune response are the lymphocytes - the B and T cells.
In the lymph nodes cytotoxic T cells encounter dendritic cells displaying epitope on MHC-I. Activating antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells that are able to induce apoptosis in body cells displaying epitopes of foreign antigen on their surface such as virus-infected cells cells with intracellular bacteria and cancer cells displaying tumor antigens. 2 An antigen fragment in complex with MHC class 2 is displayed on the B cells surface.
Such as skin the gastrointestinal tract the respiratory tract the. 1 Cytotoxic T cell response. Helper T cells primarily support other immune cells whereas cytotoxic T cells kill cells that are infected with a pathogen or are cancerous.
B lymphocytes on the other hand do not directly attack invaders. It is postulated that the initial cells that are involved in mediating both types of immunity are functionally identical in that both are antigen-reactive cells. The antigenmust encounter the B-lymphocytes T-lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cellsAPCscapable of carrying out an adaptive immune response.
T-cell mediated immunity or T-cell immunity. Typically they are multiplying within cells and may alter those cells so that the infected cell is recognized as foreign. 3 The MHC-antigen complex binds a receptor on a TH cell.
Cell-mediated Immunity is the arm of the Adaptive Immune Response which results in the generation of antigen-specific effector T-cells. The CMI system is considered to have evolved in a simpler form very early as a way of recognizing self from non-self. The CTL uses its surface receptors to recognize the infected cell.
T cells involved in cell-mediated immunity rely on antigen-presenting cells that contain membrane-bound MHC class I. An Overview of the Steps Involved in the Adaptive Immune Responses Whether humoral immunityor cell-mediated immunity there are several general steps involved in the immune responses. View the full answer.
In the case of the humoral immune response the interaction of the antigen-reactive cells with the antigen leads to the release or transfer of information to the antibody-forming cell resulting in the synthesis and secretion of. Rather they produce antibodies proteins Read More. The term cell mediated immunity CMI refers to protective mechanisms that are not primarily characterized by antibody.
Because of increasing evidence suggesting a role of cell-mediated immunity in disease resistance against many poultry disease investigation of immune systems involved in cell. The cell-mediated immunity response works by antigen presenting cells displaying an antigen on their surface that notifies the T cells that there is a pathogen in the body. CD4 T cells that activate.
Cytokines secreted by the T- helper cells activate phagocytic cells which phagocytose the pathogens and kill them. The innate immune system includes. - Cytotoxic T cells CTLs to kill virus-infected and altered self-cells.
It is the immune systems job to recognize these agents as foreign and destroy them. It is postulated that the initial cells that are involved in mediating both types of immunity are functionally identical. Part A- Correctly sort the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity.
T helper cells which express CD4 on their surface and cytotoxic T cells which express CD8 on their surface. Responses to representative pathogens. 1 Immunoglobulin receptors on the B cell recognize and bind the antigen.
Immunity cell mediated The immune system is a network of cells and organs that work together to protect the body from infectious organisms. Cell mediated immunity is provided by A B-Lymphocytes B Plasma cells C Interferon D T-Lymphocytes T-Lymphocytes Cell-mediated immunity is facilitated by the T-helper and cytotoxic T-cells. The Cell-Mediated Immune Response Basic Steps of Cell-Mediated IR CD8 CD4 MHC cl.
Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity in order. - NK cells and Macrophages 2 Delayed-type hypersensitivity DTH. Cell-mediated immunity involves the destruction of body cells that are infected with pathogens or have become damaged or cancerous.
Many different types of organisms such as bacteria viruses fungi and parasites are capable of entering the human body and causing disease. With increasing need for the development of vaccines against many poultry diseases it is important to understand host immune mechanisms involved in protection against diseases. Cell-mediated immune responses involve the destruction of infected cells by cytotoxic T cells or the destruction of intracellular pathogens by macrophages more The activation of naive T cellsin response to antigen and their subsequent.
Cell-mediated immunity is an adaptive cellular response to prevent the spread of infection. This activates the B cell. Cell-Mediated Immune Response 1.
Unlike humoral immunity cell-mediated immunity does not depend on antibodies for its adaptive immune functions. Hence the correct option is D. The literature concerned with the types of cells that participate in the humoral and cell-mediated immune response has been reviewed.
Cell-mediated immunity so named because the T cells themselves latch onto the antigens of the invader and then initiate reactions that lead to the destruction of the nonself matter.

Biol 1353 Exam 4 Mastering Ch 17 Flashcards Quizlet

Biol 1353 Exam 4 Mastering Ch 17 Flashcards Quizlet
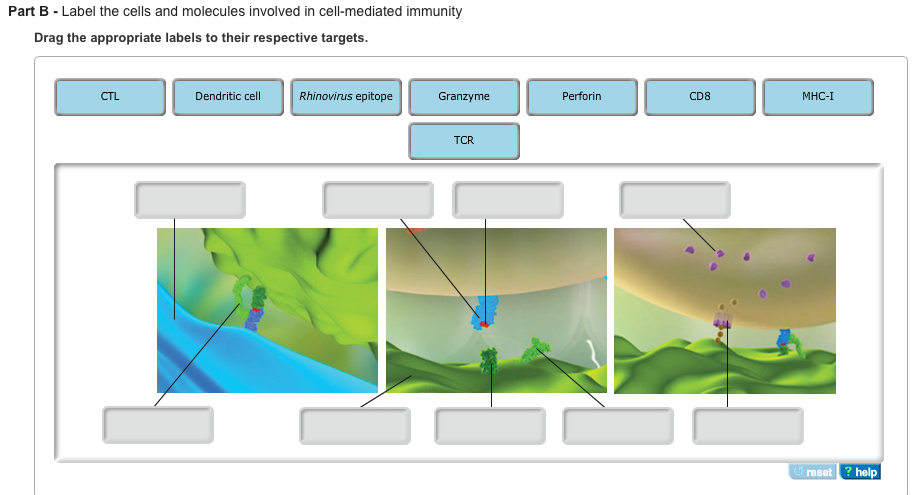
Solved Label The Cells And Molecules Involved In Chegg Com

Steps Involved In Humoral Immune Response Or Antibody Mediated Immune Response
No comments for "Correctly Sort the Steps Involved in Cell Mediated Immunity"
Post a Comment